What is an evaporator?
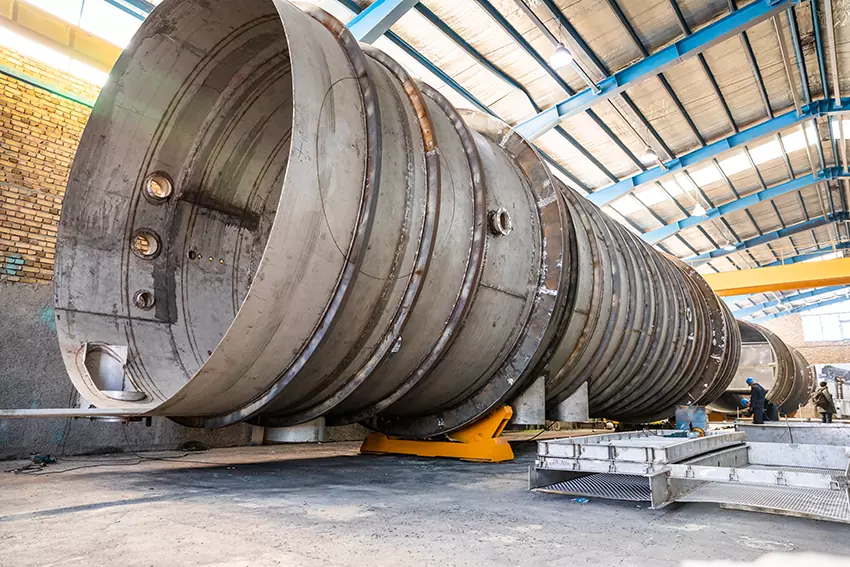
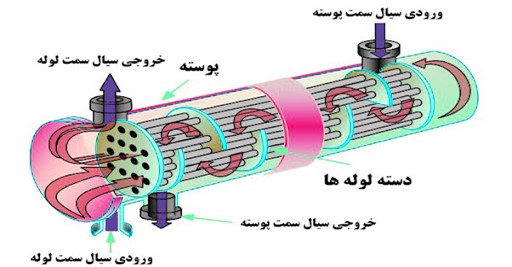
In answer to the question what is an evaporator device and how does it work, it can be said that it is a type of heat exchanger in which a liquid fluid enters a group of pipes (coils) and because it has low pressure, it absorbs the least heat from the surrounding fluid. The tubes (the fluid around the tubes can be a gas such as air or a liquid such as water and)) reach their boiling point and evaporate, thus changing phase from liquid to gas and therefore evaporating. It is also called a catalyst because the purpose is to evaporate the incoming fluid into the coil. Evaporator performance depends on the type of fluid, surface, pipe material, temperature difference, etc. it depends. The operation of the evaporator is described in more detail below. How the evaporator works in this text is described in two types of shell and tube (blue or wet) and fan (air or cold or dry air).
Evaporator application in industry in 2 different modes
Evaporators are used in two different ways in industry. In the first case, it is used as an evaporator of the fluid inside the pipes (ie, the purpose is to convert the liquid entering the coil from liquid to gas by evaporating the hot fluid around the coil, or so-called evaporating) and in The second case, due to the absorption of heat from the fluid around the coil, reduces its temperature and, as a result, cools the fluid around the coil.
1 . How the evaporator works as an evaporator
If the evaporator is used as an evaporator, the fluid to be evaporated (any liquid fluid) enters the coil (a bunch of tubes) and at a pressure approximately equal to or greater than atmospheric pressure and by taking heat from the hot fluid ( Hot water or hot steam or any gas or liquid with high temperature) evaporates around the coil, which is widely used in food, pharmaceutical, chemical and any other industrial applications as an evaporator.
۲ . Evaporator function as cooling device
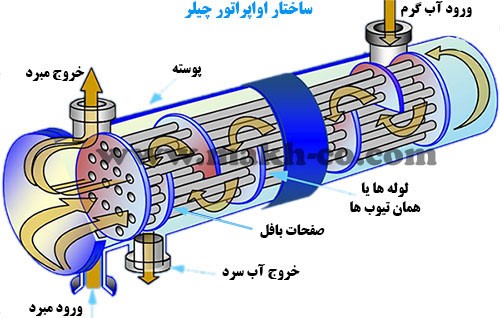
As mentioned, in one case the evaporator can be cooling. In fact, by flowing refrigerant such as Freon gas R22 or R407C and… inside the coil and flowing air by fan (in fan type) or water (in shell and tube type) by pump around the coil, refrigerant at normal ambient temperature and At a pressure lower than atmospheric pressure, it absorbs the heat of air or water and lowers the temperature of air or water. The reason for reducing the refrigerant pressure in the coil by methods such as the use of expansion valve is that the refrigerant has the property of evaporating at low pressures by taking heat from a fluid with ambient temperature (such as water or air) and from liquid to liquid. Gas change phase.
If the refrigerant cools the air by taking heat from the air, it can be used as a refrigeration evaporator or cooling air conditioner (coil dx).
Example of its use in refrigeration:
And if the refrigerant cools the water by taking heat from the water, it can be used in the chiller to cool the water.
The role of three important factors in evaporator performance
Evaporator performance is influenced by three important factors that are considered by engineers in its design.
1 . Pressure drop
It should have enough space for the fluid to circulate so that the pressure drop at the inlet and outlet is not large.
۲ . temperature difference
The fluids in and around the coil must have a sufficient temperature difference for the liquid inside the coil to evaporate completely.
3 . Type of fluid
Which has a direct effect on the choice of coil material and its surface area to achieve the desired amount of evaporation .




